5 foods to avoid when dealing with DVT

Deep vein thrombosis or DVT develops when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in the body. These blood clots are usually observed in the legs and can cause leg swelling and pain. However, in rare cases, no symptoms or signs can be seen. A few health conditions that affect clotting may also increase the risk of developing the condition. Food can play a role in managing DVT.
Signs
In most cases, a DVT develops in the arms or legs, and up to 30% of people with the condition do not experience any symptoms. However, in some cases, people may experience mild symptoms that may not raise concerns. So, one should look for signs like swelling in the arm or leg, larger-than-normal veins near the surface, and pain or tenderness in the arms or legs. Other common signs are red or discolored skin, abdominal or flank pain, warm sensation in the affected areas, and severe headache.
Foods to avoid
In most cases, healthcare professionals may suggest a few lifestyle modifications, including include avoiding a few foods, to better manage DVT and even prevent it.
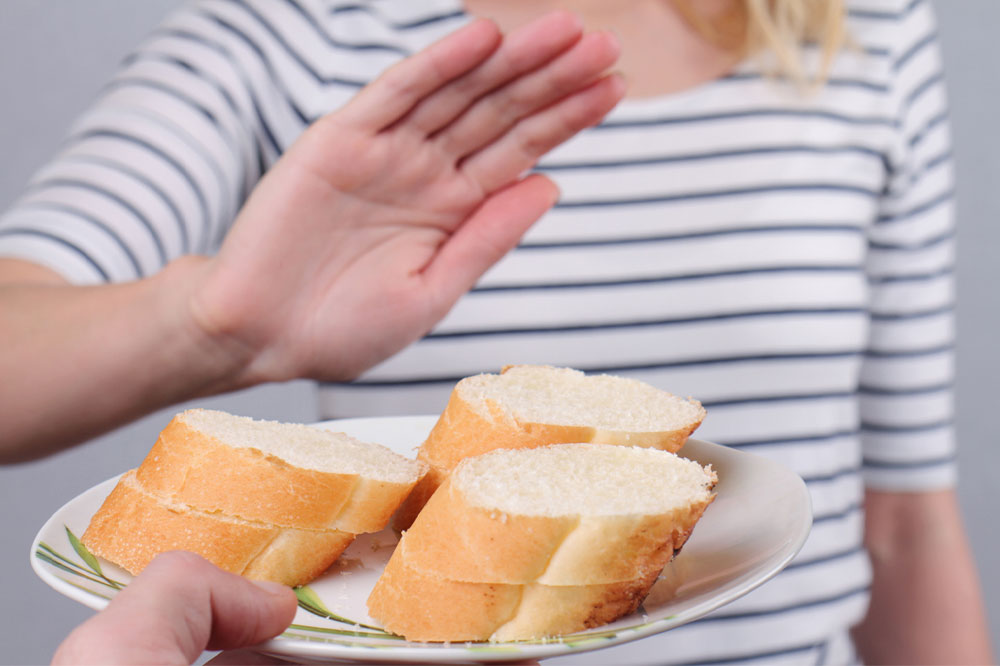
White bread
White bread and other refined foods often contain high amounts of starch. Multiple studies have suggested hydroxyethyl starch may adversely affect blood coagulation (formation of blood clots). So, when dealing with DVT, white bread and other refined items are some of the foods to avoid to prevent worsening deep vein thrombosis symptoms. Instead, one can opt for whole wheat options to meet nutritional requirements.
Cranberry juice
Fresh fruit juices such as cranberry juice may have an adverse effect on DVT patients. Cranberry juice can considerably increase the chances of internal bleeding and interfere with treatment. So, when dealing with DVT, one should avoid cranberry juice. Further, one should also avoid grape juice to maintain optimum health.
Spinach
While spinach is considered one of the healthiest vegetables, it contains Vitamin K, high levels of which can lead to the formation of blood clots and interfere with the treatment. So, one should avoid foods rich in vitamin K, such as spinach, kale, and lettuce.
Corn syrup
Added sugar is considered bad for health; however, sugar can be added to products in different forms, such as corn syrup and honey. Further, one must avoid unhealthy trans fats and salt as they can increase inflammation in the body. Honey, molasses, and even brown rice syrup can also lead to plaque buildup in the blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Potato
A staple vegetable popular among households in the country, potatoes may do more harm than good. Multiple studies have found that potato starch may have a negative effect on blood coagulation, making it a food to avoid to prevent developing deep vein thrombosis. One can alternatively add fresh fruits such as apples and oranges to their meals.
In addition to avoiding the foods mentioned above, one should consider treatment options, such as vena cava filters and compression stockings, for managing deep vein thrombosis. Doctors may recommend prescription options to make the blood thinner, enabling better blood flow around the clots.